Knowing how and when to deduct dental costs can lead to valuable tax savings. These can include your dental implants, but only if your tax circumstances allow it.

Dental implants are deductible if you are itemizing deductions on your tax return, have total medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income, and keep proper records.
If that all sounds confusing, don’t worry. Next, we’ll walk through each of these qualifiers to give you an idea if you should continue with this deduction. Then, we’ll cover how to claim it, as well as other tax-saving alternatives to this deduction.
Key Takeaways
- Dental implants, as preventative dental care, are tax deductible.
- You must itemize instead of taking the standard deduction.
- Your total medical expenses must exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income.
When Can You Deduct Dental Implants?
To claim these expenses on your federal tax return, you must meet the following specific eligibility conditions:
- Choose to itemize deductions instead of taking the standard deduction.
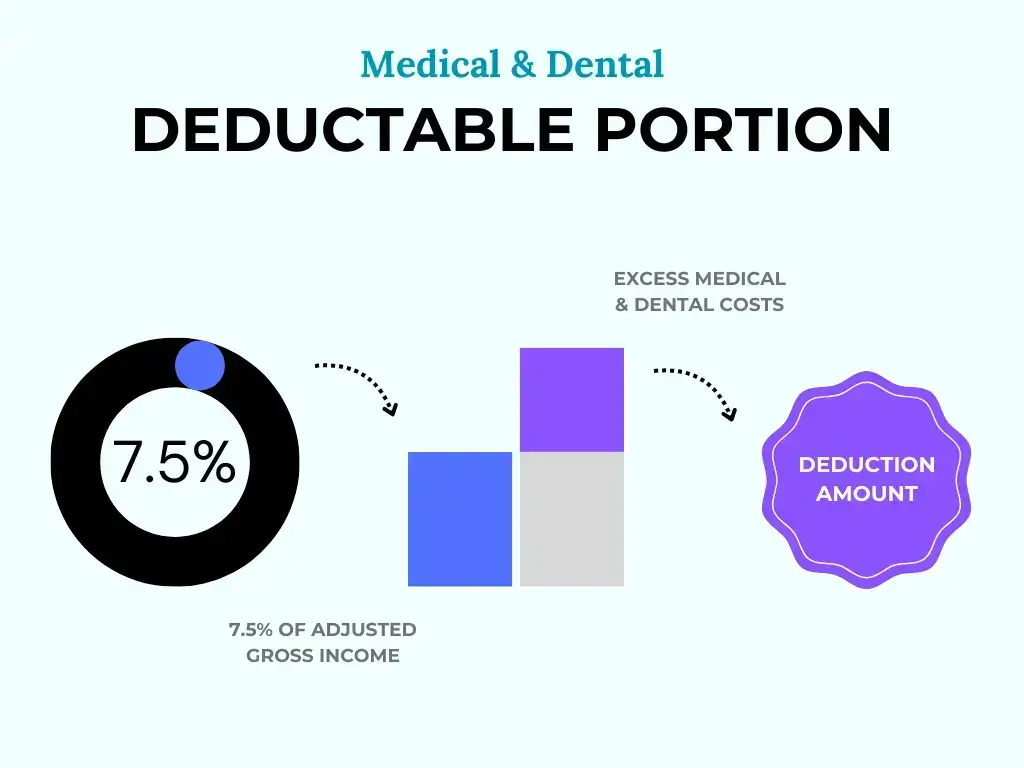
- Your total deductible medical expenses, including dental costs, must be more than 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI), which is the deductible portion.
- Keep meticulous records of all medical and dental expenses, such as invoices, bills, and comprehensive documentation, to substantiate your eligibility for this deduction.
By meeting these requisites, you can claim dental implant expenses as part of your deductible medical expenses on your federal tax return.

What Are Deductible Medical and Dental Expenses?
Tax-deductible medical and dental expenses are those that meet IRS criteria:
“Medical care expenses must be primarily to alleviate or prevent a physical or mental disability or illness. They don't include expenses that are merely beneficial to general health, such as vitamins or a vacation.”
To be eligible for the deduction, these expenses must be incurred during the current tax year, covering costs for yourself, your spouse, or your dependents, depending on your filing status.
See this list from the IRS for a complete list of deductible medical expenses.
How Do You Claim It?
To claim deductions for dental expenses on your federal income tax return, you need to follow these steps:
- Report your dental expenses as an itemized deduction on the section Schedule A of your Form 1040.
- Calculate your total deductible medical and dental expenses according to the IRS guidelines for eligible expenses outlined in IRS Topic No. 502.
- After determining your total adjusted gross income for the tax year, multiply this figure by 7.5%.
- Subtract this amount (7.5% AGI) from your total deductible medical and dental expenses. If the final amount is greater than zero, include it in your Schedule A as the deductible amount.
Here's a Short Example
Let’s say your total deductible medical and dental expenses are $20,000 for the current tax year, and you have an adjusted gross income of $100,000.
- Calculate your 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income:
- Subtract the 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income from total deductible medical expenses:
- Because the final amount is greater than zero ($12,500), you can include this amount as an itemized deduction for medical and dental expenses in your Schedule A of Form 1040.
In this example, if the total medical and dental expenses didn’t exceed $7,500, deducting dental implants would not be possible using Schedule A. Read on for more strategies.
Other Methods of Deduct Dental Implants Using a HSA & FSA
If you cannot use the itemized deduction above, then Health Savings Accounts (HSA) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSA) present another tax-saving alternative for your medical and dental expenses.

If you have a Health Savings Account (HSA), you can use funds from the account to pay for qualified medical expenses, including dental implants. Contributions to an HSA are tax-deductible, and withdrawals used for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.

If you have a Flexible Spending Account (FSA), you may also be able to use funds from the account to cover the cost of dental implants. However, FSA funds must typically be used within the plan year or any applicable grace period, so it's essential to plan accordingly.
It’s an excellent idea to speak with a CPA to learn if these accounts could be a valid alternative to claiming the itemized deduction we discussed above.
If you already have an HSA or FSA, you can check the expense eligibility list for FSAs here and the list for HSAs here.
You may not include expenses you allocated to your HSA or FSA in the Medical and Dental Expenses itemized deduction.
Conclusion: Can You Deduct It?
Yes, dental implants can be claimed as a tax deduction if you itemize your deductions and your medical and dental expenses are greater than 7.5% of your Adjusted Gross Income. You must report your dental expenses on Schedule A of Form 1040 to claim this deduction.
Seek advice from a CPA or other certified tax professional if you are unclear if you meet all qualifications. They can assist you in submitting claims for all appropriate dental and medical costs.